Scientists are pretty pumped about these five super materials that have the capacity to alter life on earth and in space.
Silica aerogel
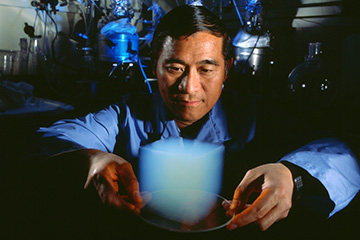
Sometimes called “frozen smoke,” silica aerogel is 99.98 percent air and can trap heat with its air pockets. Potential applications: Biotechnology, insulation (Mars fans want to use it to build warm, UV-proof settlements for humanity near the Red Planet’s ice caps)
Phosphorene nanoribbons
These tiny flexible ribbons of crystalline phosphorus can be a single atomic layer thick and 100 atoms across, but up to 100,000 atoms in length. Potential applications: Turbocharging battery power and capacity in electric vehicles and aircrafts
Black gold
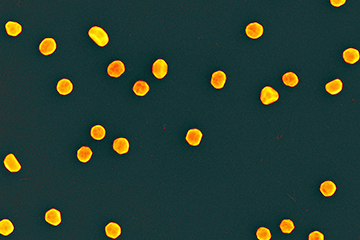
Created by Indian scientists by rearranging the size and gaps between gold nanoparticles, black gold has the unique capacity to absorb light and carbon dioxide.
Potential applications: Artificial photosynthesis, solar energy harvesting, desalinating seawater
Smart composite structures

It’s a technology that embeds fiber optic sensors within advanced composite materials. The sensors can be used to monitor real-time conditions, such as internal strain or excessive vibrations when loading. Potential applications: Building engineering and aircraft safety
Borophene
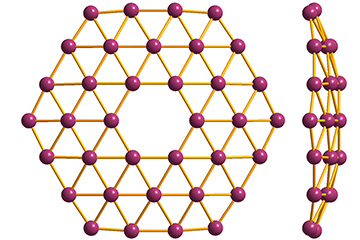
Derived from boron, this two-dimensional superconductor is only one atom thick and is thought to be twice as strong and more flexible than graphene. Potential applications: More powerful lithium-ion batteries, hydrogen storage, catalytic chemistry